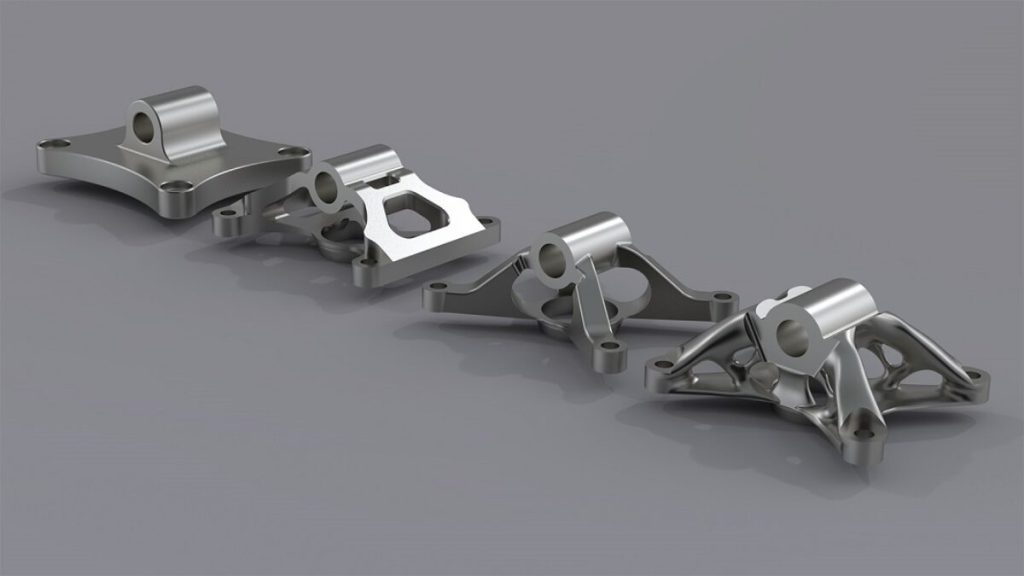
In the era of rapid digital transformation, product engineering is evolving faster than ever. Among the technologies driving this evolution, generative design stands out as a breakthrough that merges artificial intelligence, data science, and advanced simulation to create optimized products beyond human imagination. Generative design uses algorithms to automatically generate thousands of design alternatives based on given constraints, such as materials, strength, weight, and manufacturing methods. According to Autodesk, this process helps engineers discover innovative solutions that maximize performance while minimizing costs and environmental impact.
Table of Contents
1. Accelerating Innovation Through Algorithmic Creativity
Traditional design workflows rely heavily on iterative human effort and experience. Generative design, powered by AI and cloud computing, changes this process by exploring countless possibilities simultaneously. Instead of manually testing every variation, the software evaluates thousands of configurations in hours, allowing engineers to focus on selecting the best outcome. A study by the MIT Technology Review highlights how generative algorithms can boost design speed by over 70%, significantly shortening product development cycles. This acceleration enables faster innovation, especially in sectors like automotive and aerospace, where time-to-market is critical.
2. Driving Sustainability Through Resource Optimization
Environmental sustainability is no longer optional in modern engineering. Generative design helps achieve this by minimizing material waste and energy consumption. Through AI-driven simulations, engineers can create lightweight structures that use less material without sacrificing durability. For example, Airbus applied generative design to redesign aircraft partition panels, achieving a 45% reduction in weight. This directly lowered fuel consumption and carbon emissions, proving that sustainability and efficiency can coexist. As global industries pursue net-zero targets, technologies like generative design will play a central role in optimizing resources for greener production.
3. Enabling Customization at Industrial Scale
One of the biggest advantages of generative design is its ability to merge mass production with customization. Manufacturers can now produce components tailored to specific users or operating conditions without the need for manual redesign. This concept, known as mass customization, has already been adopted by leading manufacturers. General Motors used generative design to develop lightweight automotive parts that were both stronger and easier to produce. This approach enables scalable personalization, allowing companies to cater to different market segments while maintaining manufacturing efficiency.
4. Enhancing Performance and Reliability
Beyond aesthetics and sustainability, generative design also optimizes performance. The algorithmic approach ensures that every curve, joint, and hole serves a purpose backed by data. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory has used generative design to create 3D-printed components capable of withstanding extreme conditions during space missions. These parts demonstrate improved stress distribution and reduced weight, contributing to safer and more reliable spacecraft. In the automotive and industrial machinery sectors, similar principles are helping engineers build products that are lighter, stronger, and longer-lasting.
5. Seamless Integration with Additive Manufacturing
Generative design and additive manufacturing (3D printing) are deeply interconnected. The complex geometries generated by algorithms often cannot be produced using traditional machining, but they fit perfectly with additive manufacturing techniques. According to McKinsey & Company, combining generative design with 3D printing can cut prototyping time by nearly 80%. This synergy reduces development costs and accelerates innovation cycles. Industries like medical devices, consumer electronics, and aerospace are already leveraging this integration to bring highly optimized products to market faster than ever before.
The Future of Generative Design in Product Engineering
Generative design is evolving from an experimental concept to a mainstream engineering practice. As cloud computing becomes more accessible and AI algorithms grow more sophisticated, the scalability of generative design tools will continue to expand. Platforms like Siemens NX and PTC Creo are integrating real-time simulation, machine learning, and sustainability metrics into their systems, giving engineers more control and insight into every stage of the process. In the near future, generative design will not only optimize structures but also align them with business goals, environmental standards, and user experience metrics.
Conclusion
Generative design represents a fundamental shift in how products are imagined and engineered. By merging AI-driven computation with human creativity, it empowers designers to explore new territories of innovation that were once impossible to reach through conventional methods. The result is a design process that is faster, more efficient, and more sustainable. As more industries adopt this technology, generative design will redefine the boundaries of product engineering and serve as a cornerstone of intelligent manufacturing in the coming decade. Also Check How Edge AI Is Powering the Future of Smart Cities 2025






1 thought on “5 Ultimate Ways Generative Design – Revolutionizing Engineering”